Obesity is a growing health epidemic that affects millions of people globally. Over the past few decades, obesity rates have increased dramatically, contributing to a host of chronic health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. While lifestyle modifications including diet changes, increased physical activity, and pharmacological interventions can help some individuals manage their weight, these strategies often fall short for people struggling with severe obesity or related comorbidities. For these individuals, bariatric surgery has emerged as one of the most effective, evidence-based interventions for long-term weight loss and health improvement.
This comprehensive guide explores bariatric surgery in depth, including the types of procedures available, eligibility requirements, potential risks and benefits, expected outcomes, and considerations for life before and after surgery. Whether you are contemplating bariatric surgery for yourself or supporting a loved one, this guide is designed to provide accurate, expert-backed information to help you make an informed decision.
What Is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery encompasses a variety of medical procedures aimed at facilitating significant and sustained weight loss by altering the digestive system. Unlike cosmetic procedures, bariatric surgeries are not performed for aesthetic purposes; rather, they are medically indicated interventions designed to improve metabolic health. These procedures primarily work by reducing the stomach’s capacity to hold food, modifying how calories and nutrients are absorbed, or influencing gut hormones to regulate hunger and satiety.
The goal of bariatric surgery extends beyond mere weight loss. Many patients experience improvement or complete resolution of obesity-related chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. According to the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), bariatric surgery is currently recognized as the most effective long-term treatment for morbid obesity and its associated health complications.
How Bariatric Surgery Works
The mechanisms of bariatric surgery vary depending on the type of procedure, but generally, they can be categorized into three primary approaches. Restrictive procedures reduce the size of the stomach, limiting the amount of food that can be consumed at one time. Malabsorptive procedures modify the digestive tract to decrease nutrient and calorie absorption. Hormonal effects are also a critical component, as surgery can alter gut hormones to enhance feelings of fullness, reduce appetite, and improve metabolic health.
These physiological changes not only facilitate weight loss but also improve insulin sensitivity, reduce chronic inflammation, and regulate blood glucose levels. Patients often experience rapid improvements in metabolic disorders, sometimes even before substantial weight loss occurs, highlighting the surgery’s significant impact on overall health.
Types of Bariatric Surgery
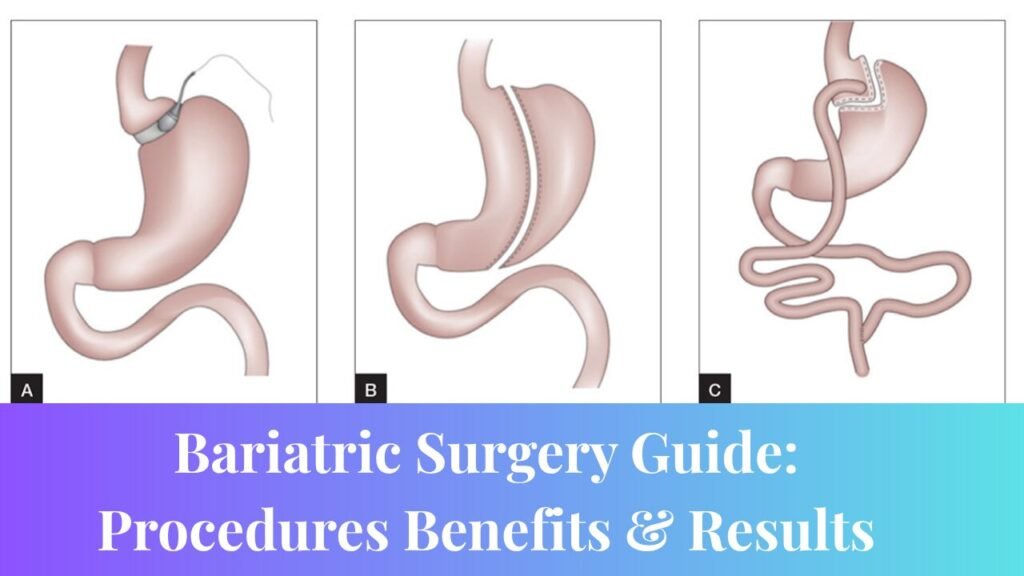
Bariatric surgery is not a universal solution; the choice of procedure depends on a patient’s individual health profile, weight loss goals, and risk factors. The most commonly performed bariatric surgeries include gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y) is one of the most widely studied procedures. It involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting a portion of the small intestine to this pouch. This approach restricts the amount of food the stomach can hold while also reducing nutrient absorption. Gastric bypass has been shown to produce significant long-term weight loss and high rates of remission for type 2 diabetes. By altering gut hormones, it also decreases appetite and promotes satiety. However, it is technically complex and carries risks such as dumping syndrome and potential vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Sleeve Gastrectomy involves removing approximately 80 percent of the stomach, leaving a sleeve-shaped tube. The reduced stomach size limits food intake and decreases the production of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for stimulating hunger. Sleeve gastrectomy is simpler than gastric bypass and avoids intestinal rerouting. Nonetheless, it is irreversible and may lead to complications such as acid reflux.
Adjustable Gastric Banding is a procedure in which a silicone band is placed around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the rate of food intake and digestion. While this procedure is reversible and involves no cutting or rerouting of the intestines, it generally results in less weight loss compared to other bariatric procedures. Frequent adjustments are required, and there is a higher rate of reoperation.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) is a complex, two-part procedure that combines sleeve gastrectomy with an extensive intestinal bypass. This surgery offers the most significant long-term weight loss and is particularly effective at resolving metabolic conditions such as diabetes. However, it carries a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies, requires a longer recovery period, and is generally reserved for individuals with severe obesity.
Who Qualifies for Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery is not intended for cosmetic purposes; it is a medical intervention for individuals with significant obesity-related health risks. Eligibility is typically determined by body mass index (BMI) and the presence of obesity-related comorbidities. Generally, candidates may qualify if they have a BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with serious obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or obstructive sleep apnea. Candidates must have unsuccessfully attempted weight loss through supervised medical programs, demonstrate no active substance abuse or untreated psychiatric disorders, and commit to long-term follow-up care and lifestyle modifications.
A comprehensive multidisciplinary evaluation is usually required, involving consultations with a bariatric surgeon, nutritionist, and mental health professional. This approach ensures that patients are physically and psychologically prepared for surgery and the significant lifestyle changes that follow.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Preparing for bariatric surgery is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring successful outcomes. Pre-operative preparation involves thorough medical evaluations, including lab tests and imaging studies, to assess the patient’s overall health and suitability for surgery. Nutritional counseling helps establish pre-surgery weight loss goals and educates patients on the dietary changes necessary for post-operative success. Psychological assessments evaluate readiness for the emotional and behavioral adjustments required after surgery.
Additionally, patients are advised to quit smoking, optimize physical activity levels, and address any underlying medical issues prior to surgery. Comprehensive preparation equips patients to manage post-operative challenges effectively and fosters long-term adherence to lifestyle modifications.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
The benefits of bariatric surgery extend well beyond cosmetic weight loss. One of the most significant advantages is the improvement or remission of obesity-related health conditions. Patients often experience dramatic improvements in type 2 diabetes, with some achieving complete remission. Hypertension and high cholesterol frequently improve, reducing the need for long-term medications. Sleep apnea symptoms often resolve, and degenerative joint pain may decrease, allowing patients greater mobility and physical comfort.
In addition to physical health improvements, bariatric surgery significantly enhances quality of life. Patients report improved emotional well-being, increased energy levels, better self-esteem, and greater participation in family and social activities. Weight loss is substantial and sustained, with most patients losing between 50 to 70 percent of excess body weight within the first 12 to 18 months and maintaining significant improvements over the long term. Research also shows a reduction in overall mortality, with fewer cardiovascular events, improved diabetes management, and decreased risk of premature death compared to individuals who do not undergo surgery.
Risks and Complications
Despite its effectiveness, bariatric surgery carries potential risks that patients must consider. Short-term risks include bleeding, infection, blood clots, adverse reactions to anesthesia, and leakage from surgical connections. Long-term risks can include nutritional deficiencies, dumping syndrome, gallstones, bowel obstruction, ulcers, and psychological challenges related to body image and eating behavior. Proper follow-up care, adherence to nutritional supplementation, and consistent medical monitoring are essential to minimize complications and ensure long-term success.
Life After Surgery
Recovery from bariatric surgery is only the beginning of a lifelong commitment to health. Dietary adjustments are critical. Patients typically begin with a liquid diet, progressing to soft foods and eventually solid foods. Emphasis is placed on high-protein, low-carbohydrate meals while avoiding sugary, carbonated, and fried foods. Daily intake of multivitamins and minerals is necessary to prevent deficiencies and maintain optimal health.
Physical activity is encouraged immediately after surgery, starting with light walking and gradually increasing to more structured exercise routines including aerobic activity and strength training. Regular physical activity supports weight loss, enhances muscle mass, and improves cardiovascular health.
Mental and emotional health is another important aspect of recovery. Many patients experience emotional fluctuations after surgery due to rapid weight changes, body image adjustments, and social dynamics. Support groups, counseling, and ongoing mental health care are crucial for addressing these challenges and promoting sustained well-being.
Real-Life Case Study
Jennifer, a 45-year-old woman, struggled with obesity for more than 15 years. With a BMI of 42 and ongoing treatment for type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea, she found traditional weight loss methods ineffective. After undergoing gastric bypass surgery, Jennifer lost 120 pounds in 18 months and was able to discontinue most of her medications. She shared, “The surgery gave me the opportunity to take back control. I can now play with my kids, walk without pain, and sleep through the night.” Jennifer’s experience highlights the transformative impact of bariatric surgery on physical health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Bariatric Surgery vs. Non-Surgical Weight Loss Methods
When comparing bariatric surgery to traditional weight loss methods such as diet and exercise alone, the differences are significant. Surgery provides rapid and sustained weight loss, often resulting in rapid improvement or remission of obesity-related comorbidities. Non-surgical methods can be effective for some individuals but often yield slower, less predictable results. Both approaches require lifestyle changes, but surgical candidates must also navigate the inherent risks associated with major medical procedures. While bariatric surgery entails higher upfront costs, the long-term health benefits and potential reduction in medical expenses often outweigh the initial investment.
Common Myths About Bariatric Surgery
There are several misconceptions surrounding bariatric surgery. One common myth is that it represents an easy way out. In reality, it requires lifelong commitment to dietary modifications, exercise, and follow-up care. Another myth is that weight regain is impossible after surgery; in truth, without sustained lifestyle changes, some patients may regain weight. The misconception that only women undergo bariatric surgery is inaccurate, as men also benefit significantly but are less likely to seek help. Finally, while pregnancy is possible after surgery, it should typically be delayed for at least 12 to 18 months to ensure stable weight and optimal nutritional status.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best type of bariatric surgery?
It depends on the patient’s health profile and weight loss goals. Gastric bypass is widely regarded for its effectiveness, while sleeve gastrectomy is safer for those with higher surgical risks.
How long does the surgery take?
Most procedures take between 1 to 3 hours, depending on the type and complexity of the case.
Does insurance cover bariatric surgery?
Yes, many insurance plans cover it if medically necessary and if the patient meets the criteria. Pre-authorization is typically required.
Can bariatric surgery cure diabetes?
It often results in remission of type 2 diabetes, particularly with gastric bypass. However, ongoing monitoring is essential.
Will I have scars after surgery?
Most surgeries are laparoscopic and result in small, minimal scarring. Open surgery may result in larger scars.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery is a medically validated, life-changing intervention for individuals suffering from severe obesity and associated health conditions. Its benefits extend beyond weight loss to include improved metabolic health, enhanced quality of life, and reduced mortality. However, successful outcomes require comprehensive evaluation, preparation, and long-term adherence to lifestyle changes. Consultation with a certified bariatric surgeon, thorough medical and psychological assessment, and ongoing support are essential components of the journey. With the right preparation and commitment, bariatric surgery can offer a transformative path to lasting health and well-being.